Can AI Teach Farmers? Exploring the Brainpower of Chatbots.
By
Shubham Durgude
AI is reshaping agronomic advisories, with chatbots like ChatGPT, DeepSeek, Gemini, and Julious assisting in crop planning, nutrient management, irrigation, and pest control. While they offer speed and data-driven insights, their accuracy and consistency remain questionable. To evaluate their reliability, we analyzed AI-generated crop calendars against standard agronomic practices, uncovering both strengths and shortcomings in AI-driven farm advisories.
AI-Powered Agronomy: How Reliable Are Chatbot Advisories?
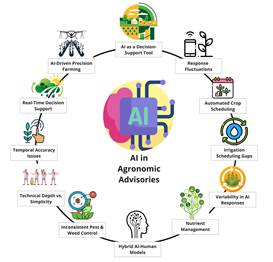
While AI brings efficiency to agronomic advisories, its effectiveness remains debatable. While it serves as a useful decision-support tool, response fluctuations and irrigation scheduling gaps pose challenges. Nutrient management also lacks consistency, with some AI models failing to balance NPK applications properly. Pest and weed control strategies remain inconsistent, and some chatbots suggest planting windows misaligned with optimal agronomic conditions. The debate between technical depth vs. simplicity persists, some AI models provide detailed insights, while others lack precision. A hybrid AI-human model is the best approach, where AI enhances decision-making but doesn’t replace expert agronomists. Future improvements must integrate real-time climate, soil health, and site-specific farm data to unlock AI’s full potential in precision farming.
Fig: AI-Powered Agronomy: the various aspects
Key Insights: How AI Chatbots Compare to Standard Agronomy
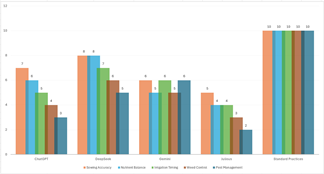
AI chatbots were evaluated on sowing accuracy, nutrient balance, irrigation timing, weed control, and pest management, with Standard Agronomic Practices serving as the benchmark, achieving a perfect 10 across all parameters. Among AI models, DeepSeek performed best, closely aligning with standard agronomy in sowing accuracy, nutrient balance, and irrigation scheduling, though it lagged in weed and pest management. ChatGPT provided balanced yet somewhat generalized recommendations, excelling in sowing and nutrients but lacking specificity in pest control. Gemini was consistent but average across all categories, offering stable yet less detailed advisories. Julious ranked the lowest, struggling significantly with weed and pest management, making it the least reliable for agronomic decision-making. While AI chatbots deliver structured and fast recommendations, their advisories still require human verification for real-world application. Among them, DeepSeek is the most agronomically sound, while Julious needs substantial improvement to match agronomic precision.
Fig: Evaluation of ChatGPT, DeepSeek, Gemini, and Julious Against Standard Agronomic Practices
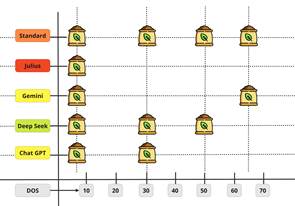
Sowing Date Variability:
Sowing timing is critical in farming, but AI chatbots seem to have their own take on it! Just for example ChatGPT is an early bird, suggesting March 1, which could invite temperature stress. DeepSeek plays it safe, recommending March 15—right in line with agronomic best practices. Meanwhile, Gemini and Julious take their time—Gemini suggests April 1, while Julious lags behind at April 15, well past the comfort zone, where heat stress and higher water demand could impact yields. Standard agronomic practices recommend March 30, striking the perfect balance. DeepSeek comes closest to this, while others… well, let’s just say they might need a refresher in crop science!
Nutrient Management Gaps:
AI-generated fertilizer recommendations are highly inconsistent, making nutrient management a gamble when relying solely on chatbots. Standard agronomic practices provide the most balanced NPK application, ensuring proper crop nutrition, but AI models vary widely—some overloading nitrogen while underapplying phosphorus and potassium, both essential for root development and grain filling. Among AI chatbots, DeepSeek is the most reliable, aligning closely with agronomic best practices. ChatGPT does fairly well but underestimates phosphorus and potassium, potentially limiting growth. Gemini underperforms across all nutrients, raising concerns about real-world applicability. Julious ranks the lowest, suggesting inadequate fertilizer doses, making it the least reliable for precision farming. Another key flaw, AI chatbots often skip split fertilizer applications, a crucial practice for nutrient efficiency, reduced leaching, and better crop uptake. Without proper nutrient timing, AI advisories risk lowering yield potential and increasing input inefficiency. While AI-powered tools provide quick and structured recommendations, they still lack the precision and agronomic depth needed for effective nutrient management. DeepSeek shows promise, but farmers and agronomists must carefully validate AI-generated advisories before implementing them in the field.
Fig: Comparison of AI Chatbot Fertilizer Split Applications vs. Standard Practices
Technical Depth & Response Stability:
AI chatbots vary widely in response length and detail, creating challenges in agronomic advisories. ChatGPT is the most verbose, offering structured but sometimes overly generalized recommendations. DeepSeek maintains stability, balancing precision and readability, making it the most reliable for detailed advisories. Meanwhile, Gemini and Julious struggle with Conciseness, often omitting critical agronomic details, with Julious ranking the lowest, providing minimal, potentially incomplete guidance. Another concern, AI responses fluctuate over time, with the same query yielding different word counts on different days, raising questions about consistency and reliability.
Chatbots briefly
- ChatGPT → Comprehensive but Overly Generalized
Provides a structured crop calendar.
Sometimes too generic, missing location-specific conditions. - DeepSeek → More Precise but Conservative
Aligns better with traditional agronomy.
Less adaptive to real-time scenarios. - Gemini → Data-Driven but Lacks Agronomic Logic
Attempts to integrate scientific principles.
Skips some essential field operations. - Julious → Fragmented and Inconsistent
Includes diverse techniques.
Major inconsistencies in scheduling, irrigation, and disease control. - Standard Practices Remain the Benchmark
While AI-generated advisories are fast and structured, their effectiveness depends on both depth and stability. DeepSeek strikes the best balance, but all AI models still require human oversight to ensure accuracy and field applicability.
Can AI Replace Agronomists?
AI chatbots offer structured agronomic planning but lack real-world precision, adaptability, and local context. They function best as decision-support tools, requiring human verification. DeepSeek aligns closest with standard practices, while ChatGPT provides detailed but sometimes vague responses. Gemini and Julious are less reliable, particularly in nutrient management and pest control. No AI model can replace expert agronomists, as they struggle with real-time decision-making and localized variability. Future advancements must integrate climate data, soil health, and site-specific conditions to improve AI-driven agronomic accuracy.
The Future of AI in Agricultural Advisory
AI is an enabler, not a replacement, in modern agriculture. A hybrid AI-human model ensures context-aware, real-time decision-making in precision farming. While AI chatbots enhance accessibility, agronomists remain indispensable for field-specific insights. Integrating localized data will make AI advisories more reliable, scalable, and practical for the future of precision agriculture.